TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. ELEMENTS OF JIG AND FIXTURE
- Body or Table (Cast iron by casting or fabricated MS bars and plates)
- Clamping device,
- Locating device,
- Tool guide
B. 3-2-1 PRINCIPAL OF LOCATION / SIX POINT LOCATION
TOP 4 ELEMENTS OF JIG AND FIXTURE
Mainly they are classified in 4 parts,
- Body or Table (Cast iron by casting or fabricated MS bars and plates)
- Clamping device,
- Locating device.
- Tool guide
1. BODY
it’s Support the workpiece. Body is fabricated from MS bars and plates or from cast iron casting. sometimes body part may be heat treated to relieve internal stresses. jig body may be of various types such as Template type, Channel type, Box type, diameter type etc.
2. CLAMPING DEVICE
The main purpose of clamping device is to hold the job pieces on jig or fixture against cutting force.
Features of a good Clamping device:-
- Low clamping pressure on job body to prevent distortion,
- Quick and simple Clamping to reduce time of loading and unloading action.
- Clamping must be rigid.
- Clamping faces must be case hardened to prevent wear.
- It must be perform many operations in one setting.
it may be various types like C-clamp, studs, Set screw, latch clamp, pivoted clamp, Double action clamp, screw clamp.
3. LOCATING DEVICE
Right location is important for accuracy of finished product. It helps to keep the job piece in correct position with respect to cutting tool. Round pin is usually used for horizontal location while shorter buttons are used for vertical location. Lock screw pins are used where pin is subjected to excessive wear and frequent replacement required. Large pins used in holes generally for locating are generally referred to as plugs with extra clearance between job and plugs. Pads and plates are used to support and locate the larger and heavier workpiece vertically. Pads and plates are fitted to jig or fixture by socket head cap screws.
4. TOOL GUIDES/ DRILL BUSHINGS
Bushing are used to guide drills, reamer or similar kind of cutting tools into the proper position on the workpiece. it’s made of hardened tool steel to make a wear resistance surface. The diameter of bushing hole should be very close to the diameter drill and length should be twice to diameter of bushing hole.
ALSO READ:- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN JIG and FIXTURE AND ITS ADVANTAGES.
3-2-1 PRINCIPAL OF LOCATION / SIX POINT LOCATION
LOCATION:-
it gives the relationship between workpiece and Jig/Fixture for correct location and maintaining the accuracy of a finished job.
PRINCIPAL OF LOCATION:-
If a rectangular block is free to move about its axis XX, YY, ZZ and can also rotate about its axis then degree of freedom of that body is SIX.
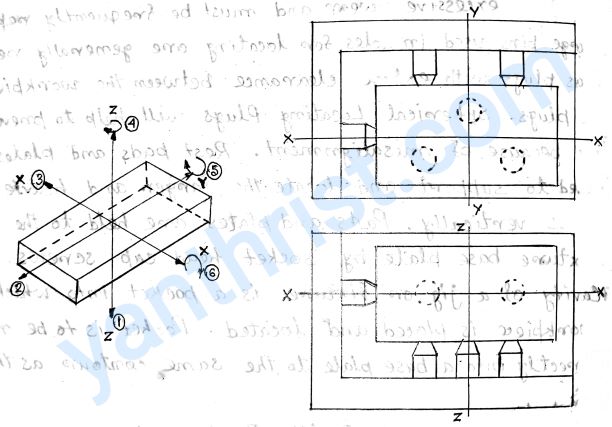
3-2-1 PRINCIPAL OF LOCATION EXPLAINED:-
Downward movement of block along ZZ is controlled by 3 supporting locating points and movements along YY & XX axis are controlled by 2 and 1 locating points respectively. Rotary movement of block about XX, YY,ZZ axis are controlled by button slide and back pins. Locating points for an uneven object is controlled by different arrangements but guiding principle are same.
The workpiece is completely restrained to move along 1, 2 and 3 direction by arranging 3 locating points in ZZ axis, 2 locating points in YY axis, 1 locating point in XX axis respectively. Hence the workpiece is also restrained to rotate about 3 axis XX, YY and ZZ i.e. three degree of movements in 4, 5 and 6. Three free movements i.e. Upward, backward and rightward are provided for locating and unloading the workpiece and during operation can be restrained by providing clamps in jig and fixture. The principal is known as 3-2-1 PRINCIPAL OF LOCATION or SIX POINT LOCATION.


