Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to precision measurement, accuracy is the key. One tool that has proven to be essential in this regard is the sine bar. It is commonly used in industries that require precise measurements, such as manufacturing and machining. Measuring angles with a high degree of accuracy is essential in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. This is where a sine bar comes into the picture. It is a simple yet effective tool that is used to measure angles with a high degree of precision. In this article, we will discuss what a sine bar is, how it works, and its applications. This article aims to explore its workings and its various uses.
What is a Sine Bar?
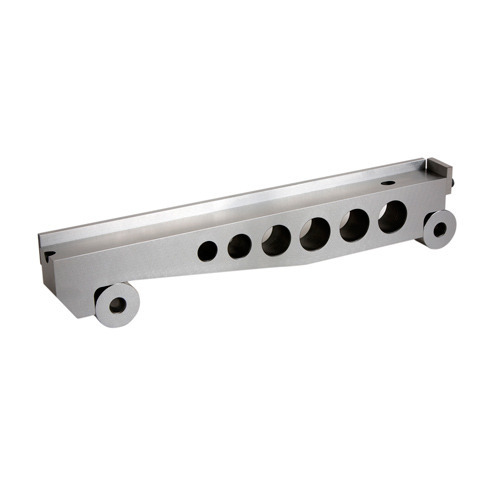
A sine bar is a precision measuring tool that is used to measure angles with a high degree of accuracy. It consists of a hardened steel bar that has two precision-ground cylindrical ends. The two ends are usually of different sizes, with the larger end being used as the reference surface.
The smaller end of the sine bar is usually attached to a gauge block, which is used to set the angle that needs to be measured. The gauge block is placed between the smaller end of the sine bar and a reference surface, such as a surface plate or a flat surface. The angle can be set by adjusting the height of the gauge block.

Design and Components of a Sine Bar
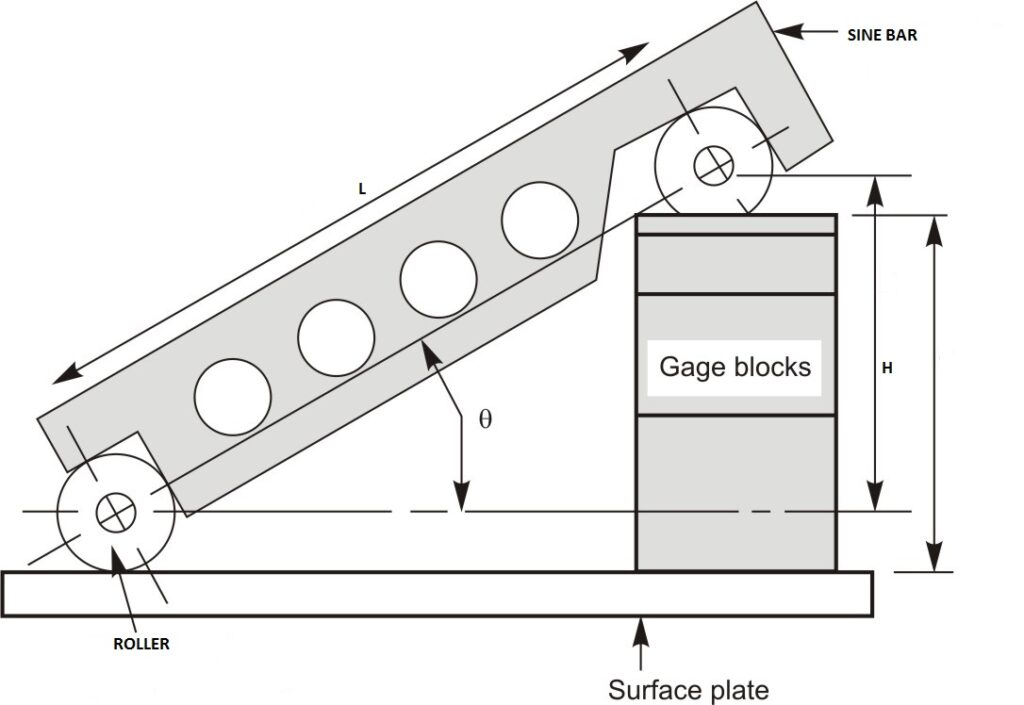
Sine Bars are usually made of high-quality steel, and they come in various sizes depending on their applications. They typically have two cylindrical bars with flat ends and a threaded hole in the center of each. Its smaller end is usually attached to a gauge block, which is used to set the angle that needs to be measured. The gauge block is made by stacking slip gauges one upon the other and it is placed between the smaller end of the sine bar and a reference surface, such as a surface plate or a flat surface. The angle can be set by adjusting the height of the gauge block. The distance between the centers of the holes is a critical measurement that determines the accuracy of the sine bar.
Sine bars are precision tools used for measuring angles and are available in several varieties to accommodate different engineering requirements. Each type serves a specific function and is designed to handle various shapes and sizes of workpieces. The primary types of sine bars include the Sine Centre, Sine Table, and Compound Sine Table.
Sine Centre: This type of sine bar is specially designed for precise angle measurements of conical objects, including those with male and female parts. A notable limitation of the Sine Centre is its inability to measure angles greater than 45 degrees, restricting its use to smaller, less acute angles.
Sine Table: Differing from the standard sine bar, the Sine Table features a broader and longer design that supports larger workpieces. Its most distinctive feature is a locking mechanism, which ensures that once the desired angle is set, the workpiece remains stable and secure, thus preventing any movement that could compromise measurement accuracy.
Compound Sine Table: Designed for handling very large and complex workpieces, the Compound Sine Table incorporates two sine tables arranged at right angles to each other. This configuration allows for the measurement of multiple angles simultaneously, enhancing flexibility and efficiency in setups that require precise multi-axis positioning.
These tools are integral to tasks that demand high accuracy in angle measurements and machining, each designed with specific features to suit different types of measurements and workpieces.
How Sine Bar Works?
To use a sine bar, the distance between the two bars is measured using a precision tool, such as a micrometer or gauge block. The bars are then placed on a flat surface, and the height of one end is adjusted using precision spacers or gauge blocks until the desired angle is achieved.
The sine bar works on the principle of trigonometry. The mathematics behind the its function involves trigonometry, specifically the sine function. The angle between the bars is equal to the inverse sine of the ratio of the height difference to the distance between the bars. The larger end of the sine bar is placed on the surface that needs to be measured, and the angle is read off a chart or calculated using trigonometric functions. The accuracy of the measurement depends on the accuracy of the gauge block used to set the angle and the flatness of the surface on which the sine bar is placed.
In simpler terms, the angle can be calculated by dividing the height difference by the distance between the bars and finding the inverse sine of the result. The sine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the opposite side of a right-angled triangle to its hypotenuse. By using this principle, it can be used to measure angles with a high degree of accuracy.
Types of Sine Bar
There are different types of sine bars available, depending on their size and applications. Precision ones are typically used in high-precision applications, whereas if accuracy is critical, standard ones are used in less demanding applications.
Applications of Sine Bars
Sine bars are commonly used in various industries that require precise angle measurements. In the machining industry, they are used to set the angle of milling heads, grinders, and other tools. In metalworking, they are used to measure the angles of saw blades, drill bits, and other cutting tools. In manufacturing, sine bars are used to align parts and machines accurately. Some of the applications of a sine bar are:
• Setting and Checking the Angle of Cutting Tools: In machining operations, it is essential to set the angle of cutting tools accurately to ensure the quality of the product. A sine bar can be used to set and check the angle of cutting tools such as milling cutters, drill bits, and lathe tools.
• Aligning Workpieces on Machine Tables: In machining operations, workpieces need to be aligned accurately on machine tables to ensure that they are cut or machined correctly. A sine bar can be used to align workpieces on machine tables, ensuring accurate machining and a high quality product.
• Measuring the Angle of Surfaces during Inspection: In industries such as aerospace and automotive, the accuracy of components is critical. A sine bar can be used to measure the angle of surfaces during inspection, ensuring that the components meet the required specifications.
• Measuring Angles in Research and Development: In research and development, accurate measurement of angles is essential to ensure the reliability and quality of products. A sine bar can be used to measure angles with a high degree of accuracy, ensuring that the products meet the required specifications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sine Bars
One of the significant advantages of using sine bars is their ability to measure angles with high accuracy. They are also relatively easy to use and do not require specialized training. However, they are limited in their applications and are not suitable for measuring complex angles or irregular surfaces.
Sine bars, while useful for certain applications, come with a set of limitations:
- The range of angles they can measure is determined by their length, which can restrict their versatility.
- For accurate measurements, they require the use of additional equipment, such as slip gauges.
- They are not ideal for extremely small or large angles.
- Their precision can be compromised over time due to wear and tear.
- Setting up a sine bar involves a more complex process compared to simpler tools like protractors.
Formula used : sin(ϴ) = H/L
• Sine θ = Opposite/Diagonal
Questions & Answers related to Sine Bar
- What is the Least Count of sine bar?
Its least count is determined by the divisions on the scale attached to it, which indicates the angle of inclination. It is typically expressed in minutes (1/60th of a degree) or seconds (1/60th of a minute)
2. What are the Specifications of a sine bar?
The specifications of a sine bar include its length, the accuracy of its angle measurement, the material it is made of (usually hardened steel), and the surface finish requirements.
3. What are the Associated components required during measurements?
When using a sine bar for measurements, associated components like a surface plate provide a flat and stable surface for placing the sine bar, slip gauges are used to set the height difference accurately, a dial indicator helps measure the height deviation, and a vernier height gauge is used to measure the reference height on the workpiece.
4. What are the various types of Sine Bar?
There are mainly two types of sine bars: single-ended sine bar, where the workpiece is placed on one end, and double-ended sine bar, where the workpiece is placed between two parallel bars.
5. What is Sine Centre?
A sine center is a precision tool used in conjunction with a sine bar for accurately locating the center of a cylindrical workpiece, enabling precise angular alignment.
6. How to use a sine bar?
A sine center is a precision to use a sine bar, place it on a flat and stable surface, set the desired angle of inclination using the scale, secure the workpiece to be measured on the sine bar, and measure the height difference between the reference surface and the workpiece using appropriate measuring tools like a dial indicator.
7. How does a sine bar measure angles?
A sine bar measures angles by utilizing its precisely angled parallel bars to provide a reference that ensures high accuracy in determining angular measurements during machining and inspection processes.
8. What is the basic design of a sine bar?
A sine bar is designed with two parallel bars that have surfaces set at precise angles, such as 5°, 10°, or 15°, to facilitate accurate angle measurements.
9. How are dial gauges used in conjunction with a sine bar?
Dial gauges are used to measure small deviations or discrepancies in height during sine bar setups.
10. What is the purpose of using a surface plate with a sine bar?
A surface plate provides a flat and stable surface necessary for accurate sine bar measurements.
11. What types of blocks are used for height adjustment in a sine bar setup?
Block gauges are used to set precise heights during the setup of a sine bar.
12. What specific tools are used to support the sine bar during measurements?
Two rollers are used to support the sine bar, allowing it to pivot accurately for angle measurements.
13. What types of gauges are needed when using a sine bar?
Both vernier height gauges and dial gauges are needed for precise measurements.
14. What components are necessary for setting up a sine bar, and what are their functions?
Necessary components include a surface plate for a stable reference surface, dial gauges for alignment and uniformity checks, block or slip gauges for precise height and length measurements, and a vernier height gauge for measuring roller heights to facilitate angle calculations.
15. How does a vernier height gauge contribute to the sine bar setup?
The vernier height gauge is used to precisely measure the height of the rollers on the sine bar, which is necessary for accurately determining angles, especially when dealing with larger components within the setup.
16. What is the purpose of block gauges or slip gauges in the setup?
Block or slip gauges are essential for providing exact standards for measuring heights and lengths, which enhances the overall accuracy of the sine bar’s functionality in setting up precise angles.
17. How are dial gauges used in the setup?
Dial gauges play a crucial role in checking the evenness of the surface and ensuring the accurate alignment of the workpiece relative to the sine bar, which is vital for precise measurement outcomes.
18. What is the role of the surface plate in a sine bar setup?
The surface plate provides a critical base for the sine bar and other components, establishing a consistent and precise horizontal reference point necessary for accurate measurements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sine bars are essential tools for precision measurement in various industries. They are designed to measure angles with high accuracy and are relatively easy to use. Different types of sine bars are available, depending on their applications, and they offer several advantages and disadvantages. Understanding how sine bars work and their various uses can help improve the accuracy and precision of measurements in different industries.
What is the range of a Sine Bar typically available in?
The typical range of available sine bar lengths generally consists of 100 mm, 200 mm, and 300 mm. These lengths allow for accurate angular measurements within their respective dimensions.
What is the difference between a Sine Bar and a Protractor?
A sine bar and a protractor are both tools used for measuring angles, but they differ significantly in precision, design, and typical applications.
A sine bar is a precision instrument crafted from a hard, rigid material like steel. It features two accurately spaced cylindrical rollers. Utilizing trigonometric functions, it calculates angles very accurately when used in conjunction with precision height blocks known as slip gauges. This device is predominantly used in high-accuracy settings such as machining and engineering, where exact angle setups are crucial.
On the other hand, a protractor is a more commonly used tool for measuring angles, and it can be found in various forms, including semi-circular or full-circle versions made of plastic or metal. It has degree markings over its surface for direct reading and is generally used without any additional instruments. While easy to use and versatile, protractors typically do not provide the same level of precision as sine bars. They are widely employed in educational settings, construction, carpentry, and for many general measurement tasks where a high degree of precision is not necessary.
In summary, the key differences lie in the tools’ precision, construction, method of use, and the typical situations in which they are used. Sine bars are essential for precise industrial tasks requiring exact measurements, whereas protractors serve well for everyday angle measuring needs across a variety of industries.
What are the limitations of a sine center in terms of measuring angles?
The sine center is a specific type of sine bar used for measuring the angles on objects with conical features, including those with both inward and outward facing surfaces. One significant constraint of this instrument is its inability to accurately measure any angle that is greater than 45 degrees.