Discover the key differences between nut vs bolt in this comprehensive guide. Learn how these essential fasteners work together, their various types, and their specific applications in construction, machinery, and everyday use.
What are Bolts?
A bolt is a type of fastener having an outside threaded circular rod designed to be used with a nut. washer to join two or more parts. Unlike screws, which create their own thread in the material, bolts require a nut to fasten securely. They are inserted through pre-drilled holes in the parts being joined and then tightened with a nut on the opposite side.

Types of Bolts
Sl No. | Type | Diagram | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anchor Bolt |  | A bolt with a threaded portion at one end and a non-threaded, eye-shaped head at the other end. Usually comes with a washer and nut, and is rust-resistant. | Used for setting light poles and fastening equipment to concrete bases. |
| 2 | Carriage Bolt |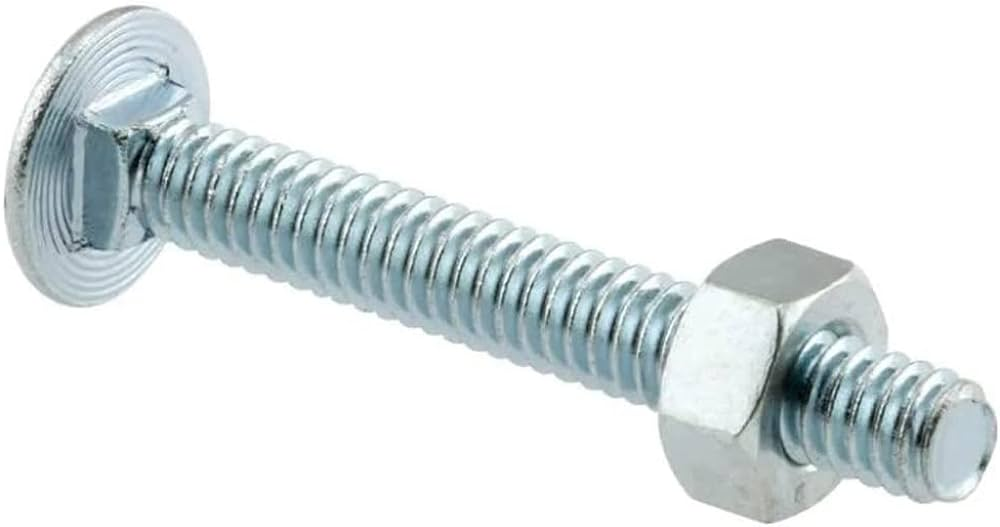  | Fully threaded with a smoothly formed head and a square or ribbed undercut to prevent rotation during tightening. | Used for fastening wood to metal. |
| 3 | Eye Bolt |  | A fastener with a rod-shaped body and a loop at one end. | Commonly used in lifting applications for heavy-duty service. |
| 4 | Hanger Bolt |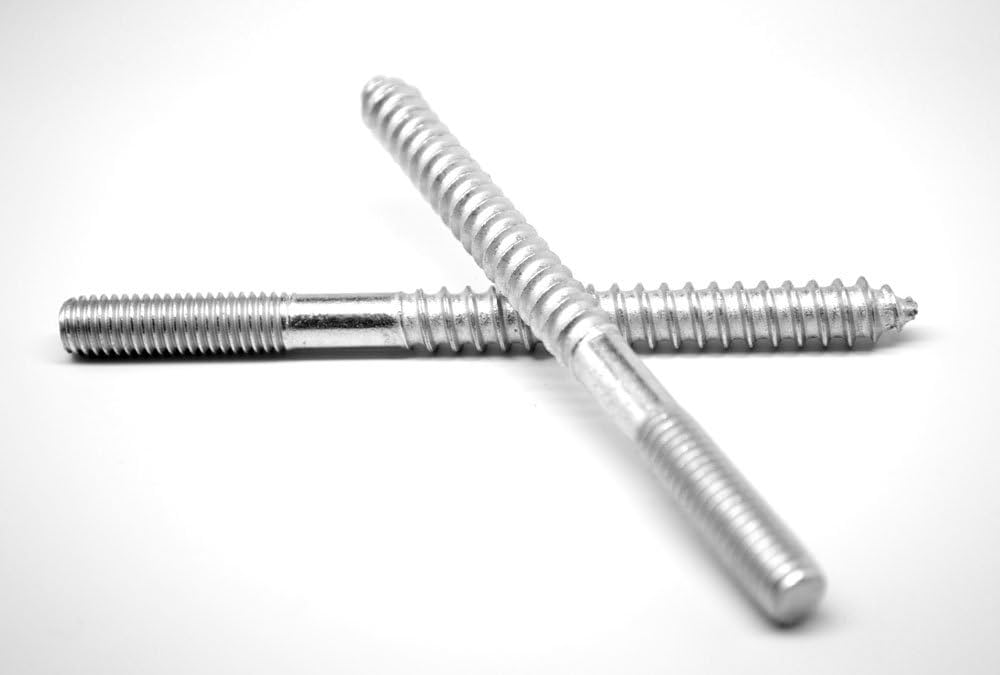  | Headless bolt with threads on both ends; one end is shaped like a wood screw. | Used in overhead, elevated applications for fastening wood and rods. |
| 5 | Hex Bolt |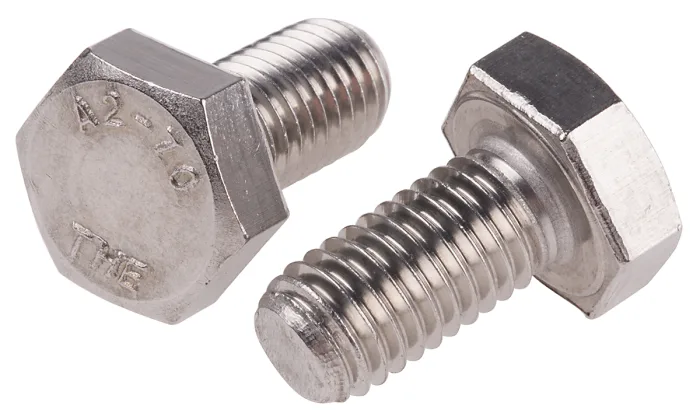  | Bolt with a six-sided head, available either fully or partially threaded. | Widely used in construction and repair of buildings and highway elements. |
| 6 | Square Head Bolt |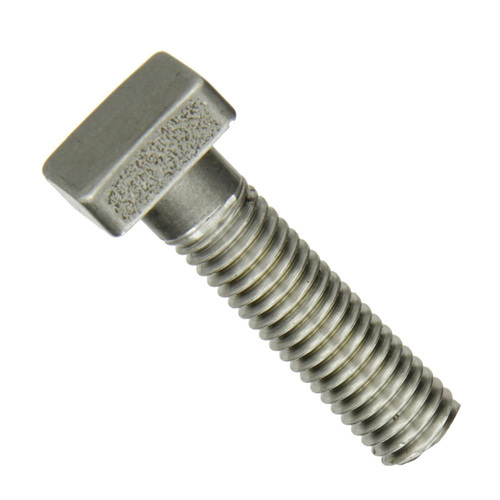  | Features a square head and a smooth shank, with fully or partially threaded options. Easier to grip with a wrench during tightening. | Used in industrial, agricultural, and construction applications. |
| 7 | U-Bolt |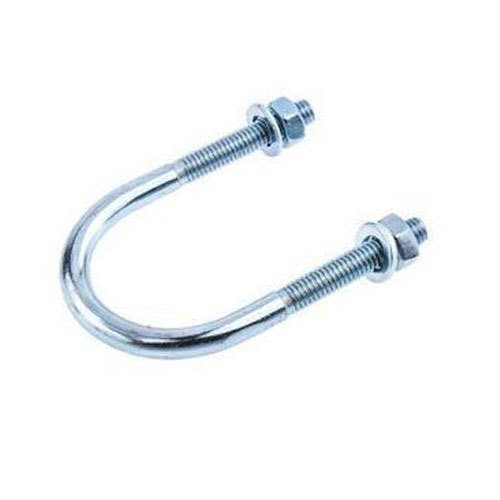  | Shaped like the letter “U” with threads on both ends. | Used for supporting pipework. |
| 8 | Lag Bolt |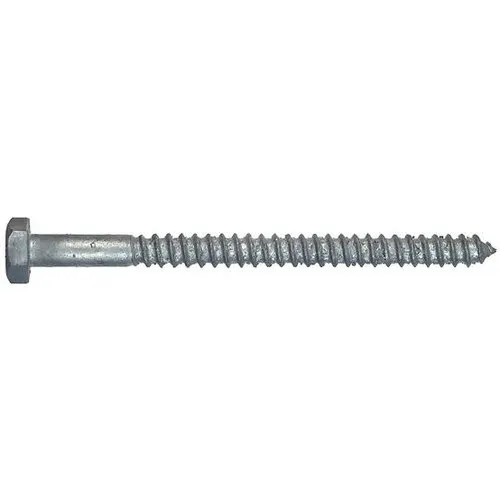  | Tough fasteners that create their own threads when penetrating wood and other soft materials. | Connecting heavy materials that bear extreme loads. |
| 9 | Flange Bolt |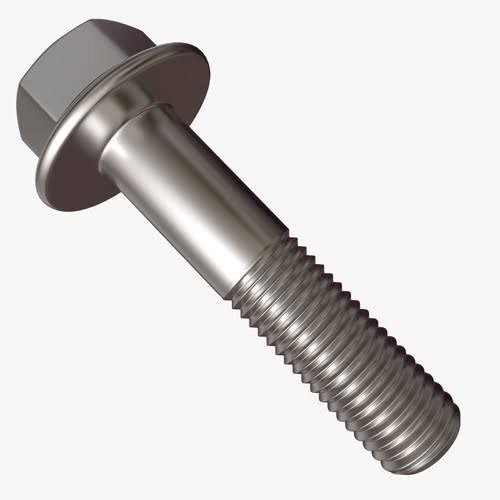  | Has a circular, washer-like flange under the head to distribute clamping force. | Used in vehicles to secure engines and transmission systems, and in piping systems to hold flange pipes together. |
| 10 | Serrated Flange Bolt |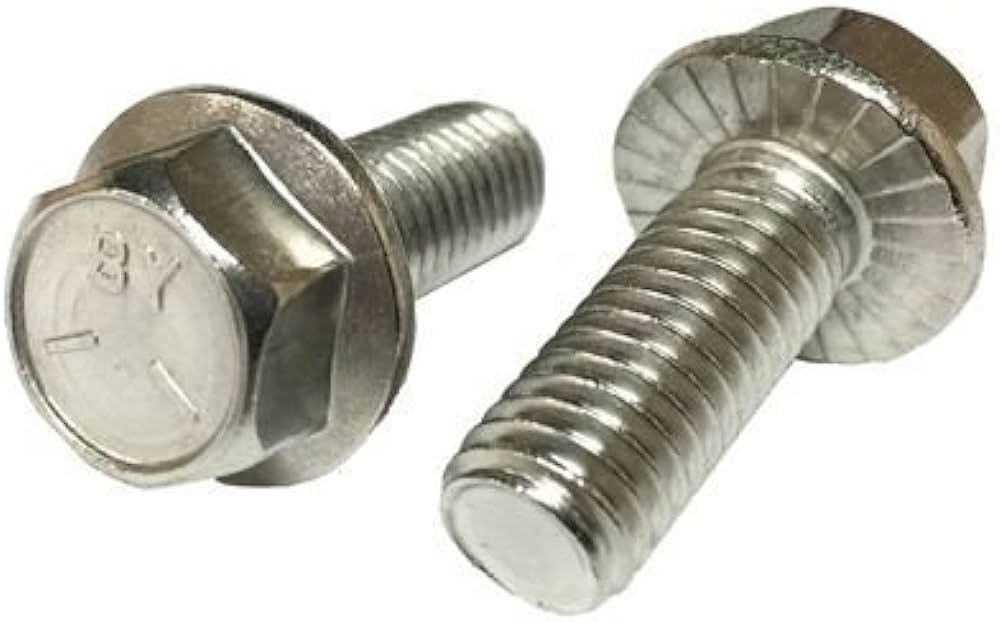  | Similar to standard flange bolts but with teeth on the flange to grip surfaces and resist vibration. | Used in mechanical and plumbing applications, and electronic product casings. |
| 11 | Plow Bolt |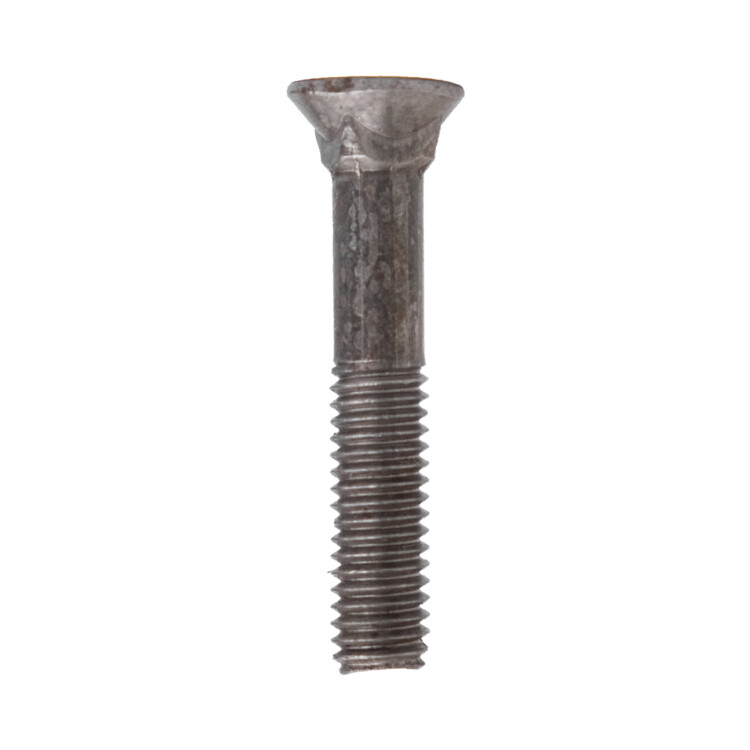  | Similar to carriage bolts but with countersunk heads and a square neck. | Used in heavy equipment like snowplows, tractors, excavators, and scoop shovels. |
| 12 | Socket Head Bolt |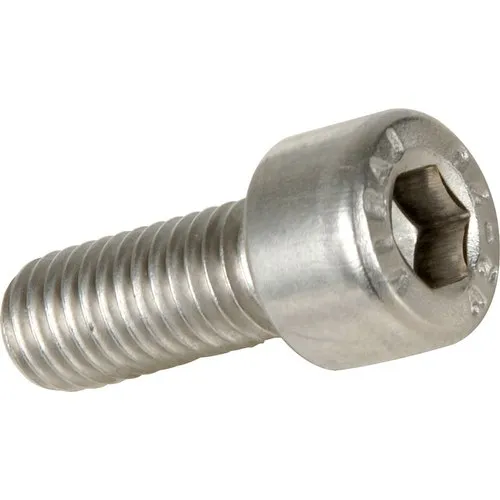  | Features a recessed slot in the head for an Allen wrench or socket tool. | Used in industrial production and assembly lines. |
| 13 | Stud Bolt |  | Headless bolts with threads on both ends of the shaft, either fully threaded or partially threaded. | Connecting equipment parts and permanent fixtures. |
What are Nuts?
A nut is a type of fastener featuring a threaded hole, specifically designed to be used with a bolt to securely join multiple parts. The assembly is held together by the friction between the threads of the nut and bolt, as well as the slight stretching of the bolt and the compression of the parts being fastened. This combination ensures a strong and stable connection.
Differences Between Nuts and Bolts
| Aspect | Nuts | Bolts |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Always used with a bolt | A solid cylindrical fastener used with a nut |
| Shape | Hollow circular cylinders with a circular cross-section | Solid cylinders with a circular cross-section |
| Threads | Internal threads | External threads |
| Size | Smaller in size compared to bolts | Larger in size compared to nuts |
| Lock Mechanism | Have lock mechanisms to prevent loosening | Do not have lock mechanisms |
| Heads | Do not have heads | Have heads for tightening and loosening |
| Forces Experienced | Experience compression forces and generally fail due to compressive stresses | Experience tensile forces and generally fail due to tensile stresses |
| Types | Hex Nut Nylon Insert Lock Nut Jam Nut Nylon Insert Jam Lock Nut Square Nut Cap Nut Acorn Nut T-Nut K-Nut Castle Nut Wing Nut Flange Nut Slotted Nut Coupling Nut etc. | Anchor Bolt Carriage Bolt Elevator Bolt Flange Bolt Hanger Bolt Hexagon Bolt (or Tap Bolt) Lug Bolt Machine Bolt Plow Bolt Barrel Bolt Shoulder Bolt Square Head Bolt Stud Bolt Timber Bolt T-Head Bolt Toggle Bolt U-Bolt J-Bolt Eye Bolts etc. |